
DOT & CROSS
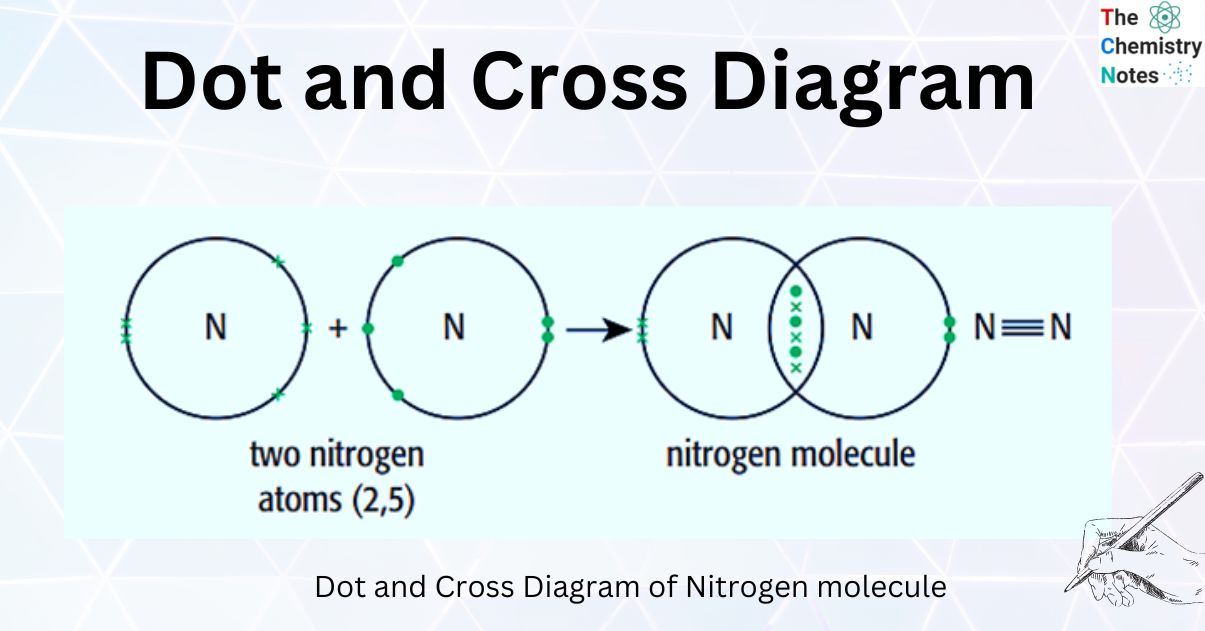
Dot-and-cross diagrams of covalent compounds in which the atoms share their valence electrons Double covalent bonding Oxygen, O2 Covalent bonding in oxygen Carbon dioxide, CO2 Covalent bonding in carbon dioxide Ethene, C2H4 Covalent bonding in ethene Triple covalent bonding Nitrogen, N2 Covalent bonding in nitrogen Dative covalent bonding
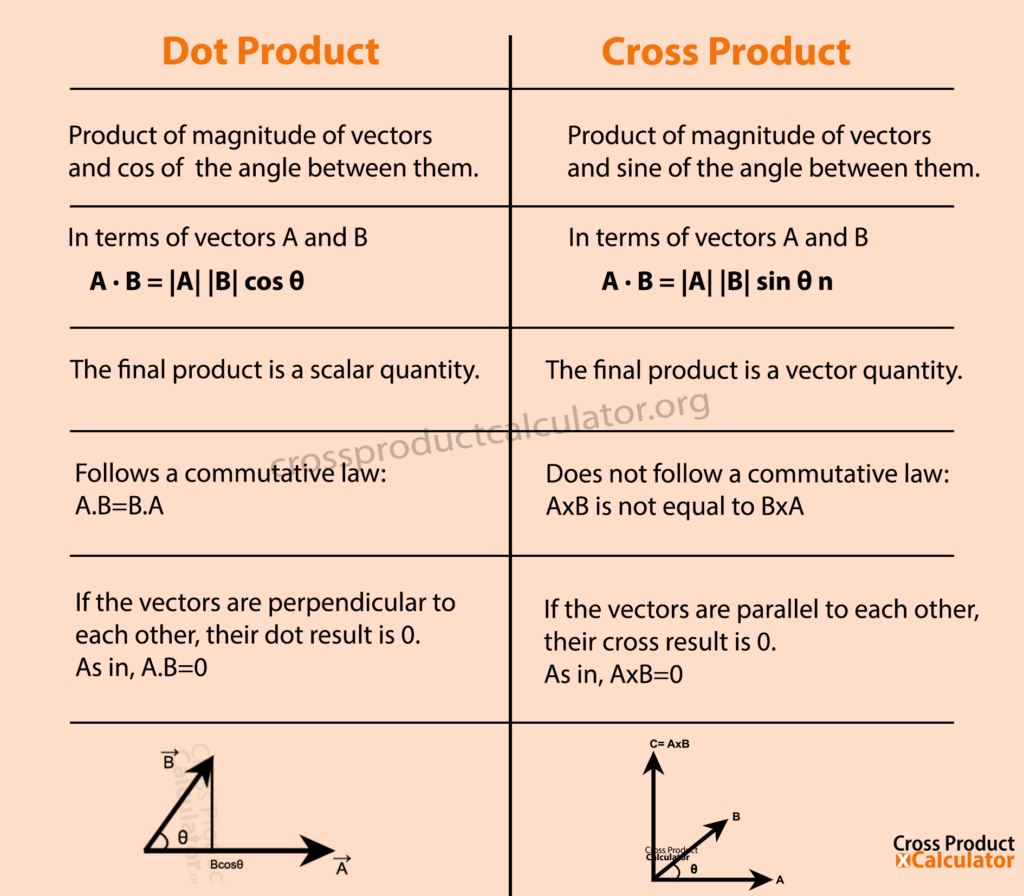
Dot Product vs Cross Product What's the Difference?
Some dot-and-cross diagrams may also not include the circles of the electron shells and show only the electrons in the outer shell. You should be able to use dot-and-cross diagrams to represent covalent bonds in: Diatomic molecules (including H 2, O 2, N 2, halogens and hydrogen halides) Inorganic molecules (including water, ammonia and carbon.
33 best ideas for coloring Dot And Cross Diagram
Dot- and- cross diagram of covalent molecule carbon dioxide (CO 2) Let's look at drawing the dot-and-cross diagram of carbon dioxide. Oxygen is in group VI of the periodic table. With 6 valence electrons, it needs 2 more electrons. So it will share 2 electrons to achieve stable octet configuration. It can share the 2 electrons with 1 atom.

Dot Cross's Instagram, Twitter & Facebook on IDCrawl
In this video, we are going to see how to draw dot and cross diagrams for covalent bonding. Specifically, we are going to draw dot and cross diagrams for H2O, NH3, CH4 and CO2. The dot.

Cross & Dot PDF download
A dot and cross diagram can model the bonding in a simple molecule : the outer shell of each atom is drawn as a circle circles overlap where there is a covalent bond electrons from one atom are.

Dot Cross Product Practice Problem YouTube
How to draw a dot and cross diagram for ammonia In NH 3, commonly known as ammonia, nitrogen forms three single covalent bonds with three hydrogen atoms. Source: © Dan Bright While you are learning how to draw dot and cross diagrams it's useful to start with something you are already familiar with: electron configuration diagrams.
.PNG)
Bohr’s Atom
Definition: The Dot Product. We define the dot product of two vectors v = a i ^ + b j ^ and w = c i ^ + d j ^ to be. v ⋅ w = a c + b d. Notice that the dot product of two vectors is a number and not a vector. For 3 dimensional vectors, we define the dot product similarly: v ⋅ w = a d + b e + c f.
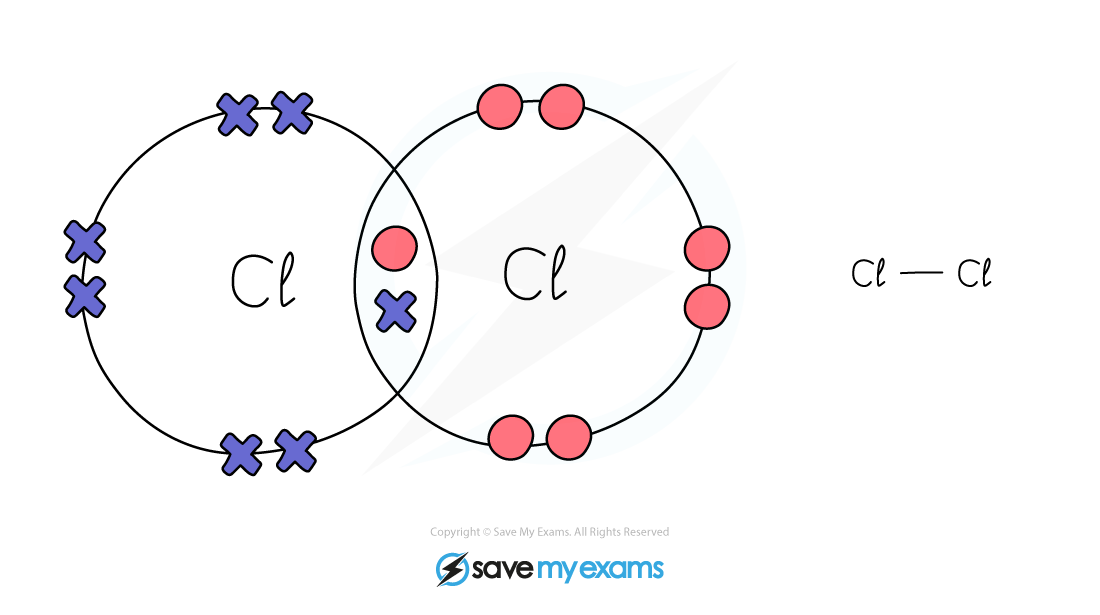
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry 复习笔记 1.7.2 Covalent Bonds Dot & Cross Diagrams
A dot and cross diagram can show the bonding in a small molecule: the outer shell of each atom is drawn as a circle circles overlap where there is a covalent bond electrons from one atom are.
Dot and Cross Diagram
Representing Dot & Cross Diagrams. Dot and cross diagrams are diagrams that show the arrangement of the outer-shell electrons in an ionic or covalent compound or element. The electrons are shown as dots and crosses. In a dot and cross diagram: Only the outer electrons are shown. The charge of the ion is spread evenly which is shown by using.

Fluorine Molecule Dot And Cross Diagram Diagram Media
In a dot and cross diagram, ions are drawn as a central nucleus, surrounded by rings of orbiting electrons (represented by either dots or crosses). The formation of ionic molecules can be shown by using dots to represent the electrons of one ion, and crosses for the electrons of another. By placing the dot of a metal ion in the outer ring of.

GeekSVGs
There are three shared spaces between the circles, so add a dot and cross to each one. This incomplete dot and cross diagram shows only the bonding pairs of electrons Finally, add in the.

Drawing Dot and Cross Diagrams
Topic Covalent bonding and dot and cross diagrams Level GCSE (or any other course for students aged 11-16) Outcomes 1. To understand how a covalent bond is formed 2. To be able to use molecular and displayed formula 3. To draw dot and cross diagrams for simple covalent molecules involving single, double and triple bonds

Cross dot to dot printable worksheet Connect The Dots
Dot & Cross Diagrams. Dot and cross diagrams are diagrams that show the arrangement of the outer-shell electrons in an ionic or covalent compound or element. The electrons are shown as dots and crosses. In a dot and cross diagram: Only the outer electrons are shown. The charge of the ion is spread evenly which is shown by using brackets.

Physical Chemistry Video Lessons
Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks Sort by: Top Voted prashanth.jayashree 12 years ago Its difficult to imagine how useful the Dot and Cross products are in real world applications. Some examples would shed a lot of light • 3 comments ( 33 votes) RKHirst 12 years ago
13+ Dot And Cross Diagram Robhosking Diagram
In dot and cross diagrams, commonly introduced at 14-16 (Figure 1b), each atom's outer shell electrons are shown in circular orbits. Covalent bonds are represented by a shared pair of electrons in an area of overlap. Neither of these models show the 3D shape of the molecule.

Dot and Cross Products YouTube
Dot and cross diagrams allow us to visualize how electrons are shared through out a molecule and from which atoms they originated, but do not tell us anything about the shape of those molecules.